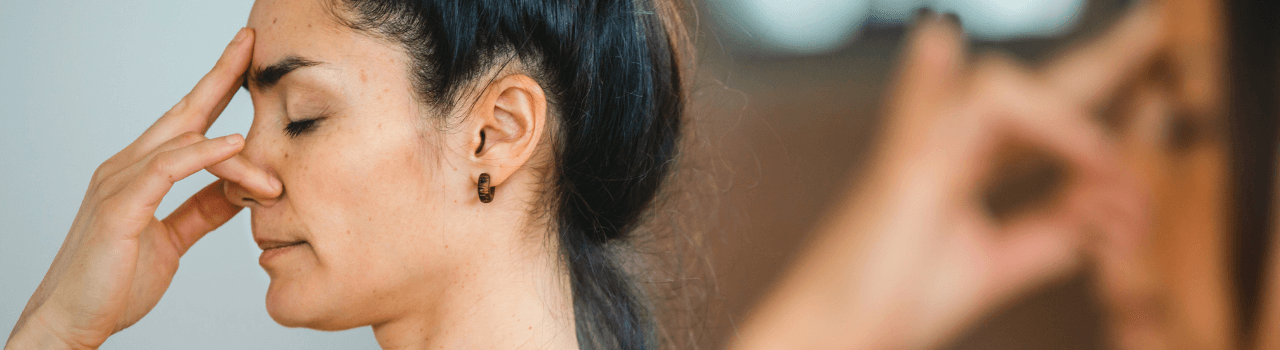Unlocking better sleep is something we all strive for, and the key to achieving it might be closer than you think. Welcome to the world of vagal stimulation, where the vagus nerve plays a pivotal role in regulating our sleep patterns.
The vagus nerve is the longest cranial nerve in the body, connecting the brain to various organs, including the heart, lungs, and digestive tract. It acts as a two-way communication highway, relaying information between the brain and the body.
Research suggests that stimulating the vagus nerve can have a profound impact on sleep quality. By activating this nerve, we can promote relaxation, reduce anxiety, and improve overall sleep duration and depth.
Various methods can be used to stimulate the vagus nerve, from simple breathing exercises and meditation techniques to more advanced interventions like vagus nerve stimulation devices.
In this article, we will explore the fascinating world of the vagus nerve and how vagal stimulation can unlock better sleep. Whether you're a sleep-deprived parent, a busy professional, or simply looking to optimize your sleep, understanding and harnessing the power of the vagus nerve can lead to more restful nights and rejuvenating days.

Functions and role of the vagus nerve in the body
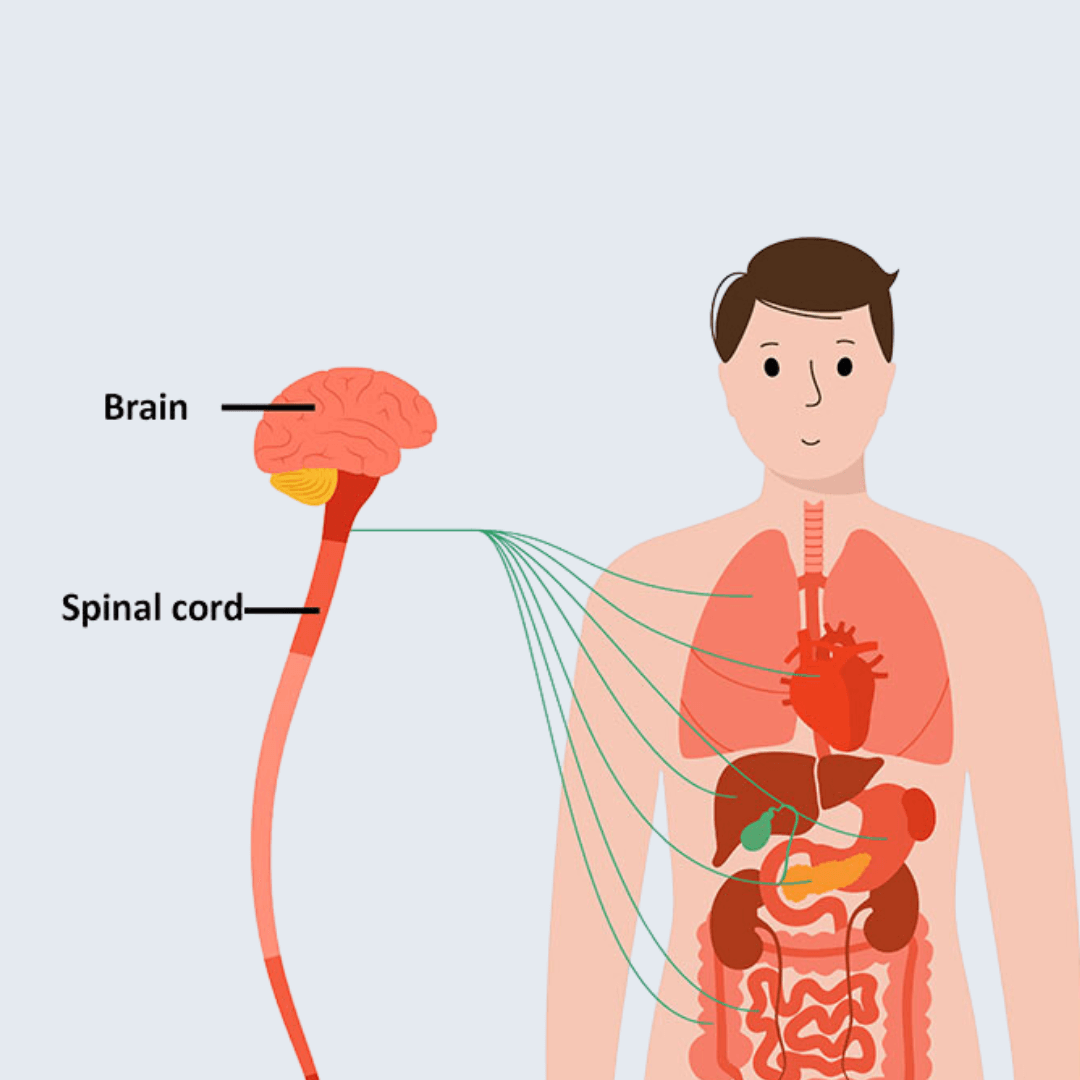
The vagus nerve, also known as the tenth cranial nerve, is a crucial component of the autonomic nervous system. It plays a vital role in regulating various bodily functions, serving as a crucial communication link between the brain and the organs.
Originating in the brainstem, the vagus nerve extends down through the neck, chest, and abdomen, innervating the heart, lungs, stomach, and other internal organs. This extensive network allows the vagus nerve to influence a wide range of physiological processes, including heart rate, breathing, digestion, and even immune function.
By transmitting information in both directions, the vagus nerve acts as a two-way street, relaying signals from the brain to the body and vice versa. This bidirectional communication is essential for maintaining homeostasis, the body's ability to maintain a stable internal environment. When the vagus nerve is functioning optimally, it helps the body adapt to changing conditions and respond appropriately to various stimuli.
Understanding the link between the vagus nerve and sleep
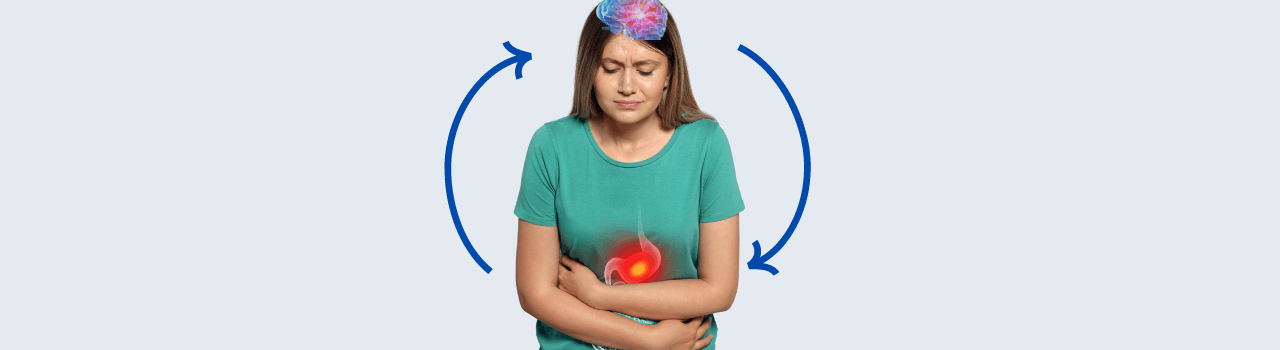
The vagus nerve's influence extends to the regulation of sleep and wakefulness. Numerous studies have demonstrated the strong connection between vagal activity and sleep patterns.
One of the primary ways the vagus nerve impacts sleep is through its role in the parasympathetic nervous system, which is responsible for the body's "rest and digest" functions. During sleep, the parasympathetic nervous system becomes more dominant, allowing the body to rest, repair, and regenerate. The vagus nerve plays a crucial part in this process by promoting relaxation and reducing arousal levels.
When the vagus nerve is stimulated, it can trigger a cascade of physiological changes that promote sleep. These changes include a decrease in heart rate, a drop in blood pressure, and an increase in heart rate variability (HRV) - a measure of the fluctuations in the time interval between consecutive heartbeats. Higher HRV is associated with better sleep quality and overall well-being.
Benefits of vagal stimulation for sleep improvement
Stimulating the vagus nerve can have a profound impact on sleep quality, offering a range of benefits that can improve the overall sleep experience. Research supports that vagal stimulation can enhance relaxation, reduce anxiety, and promote deeper, more restorative sleep by influencing the parasympathetic nervous system.
One of the primary benefits of vagal stimulation is its ability to reduce anxiety and stress, which are common culprits behind sleep disturbances. By activating the parasympathetic nervous system, vagal stimulation can trigger a relaxation response, calming the mind and body and creating an optimal environment for restful sleep.
Furthermore, vagal stimulation has been shown to enhance the quality of sleep, increasing the duration of deep, restorative sleep stages. Deep sleep is crucial for physical and cognitive restoration, as it allows the body to repair tissues, consolidate memories, and regulate hormones essential for overall health.
Techniques for stimulating the vagus nerve
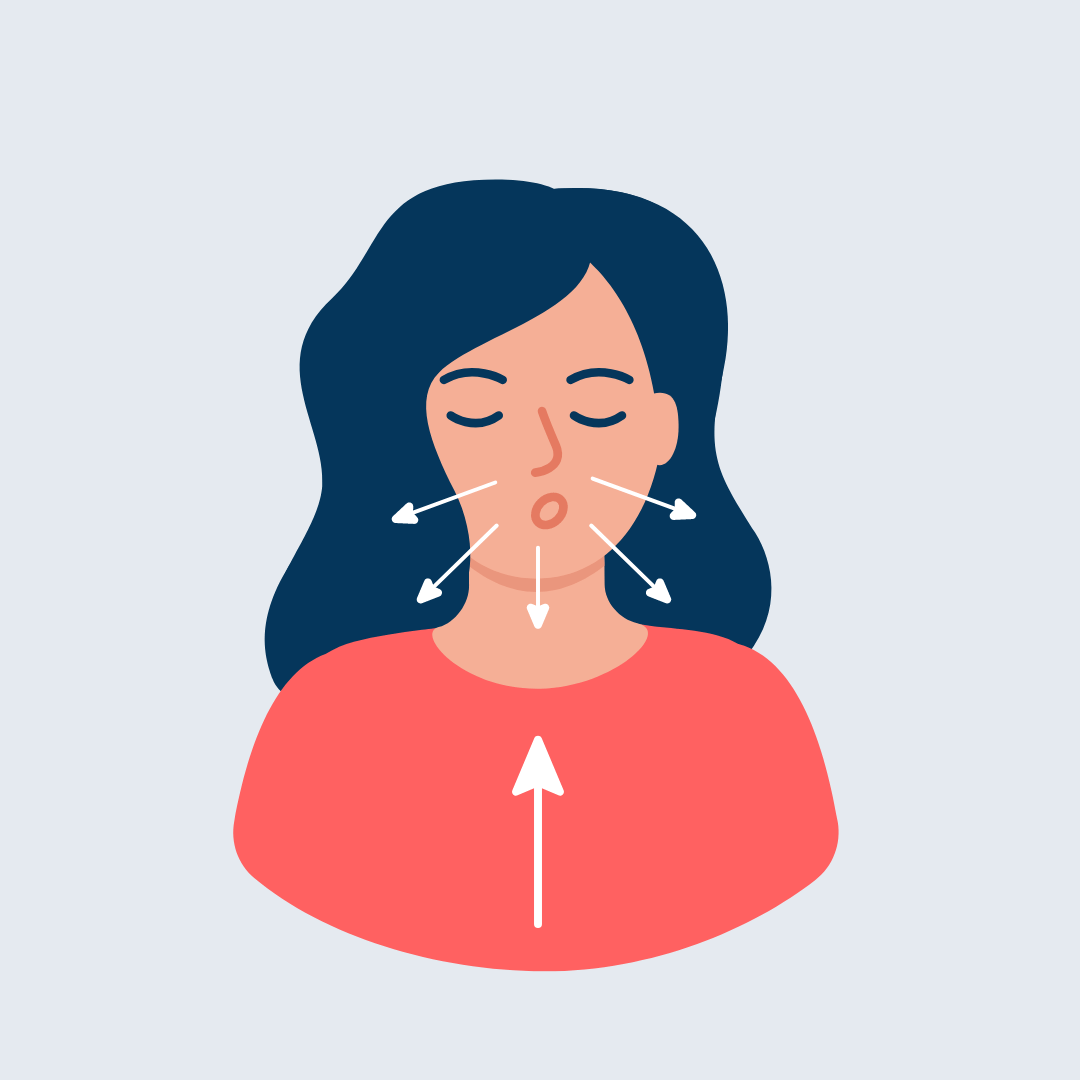
There are several techniques and methods that can be used to stimulate the vagus nerve and unlock the benefits for better sleep. These range from simple, self-care practices to more advanced medical interventions.
One of the most accessible and widely-practiced techniques for vagal stimulation is deep breathing. By taking slow, deep breaths and focusing on the sensations of the breath, you can activate the vagus nerve and trigger the parasympathetic nervous system's relaxation response. This can help lower stress levels and promote a state of calm, setting the stage for more restful sleep.
Another effective technique is gargling or humming. The act of gargling or humming engages the muscles in the throat and neck, which are innervated by the vagus nerve. This stimulation can help increase vagal tone and enhance the nerve's ability to regulate bodily functions, including sleep.
Breathing exercises for vagal stimulation
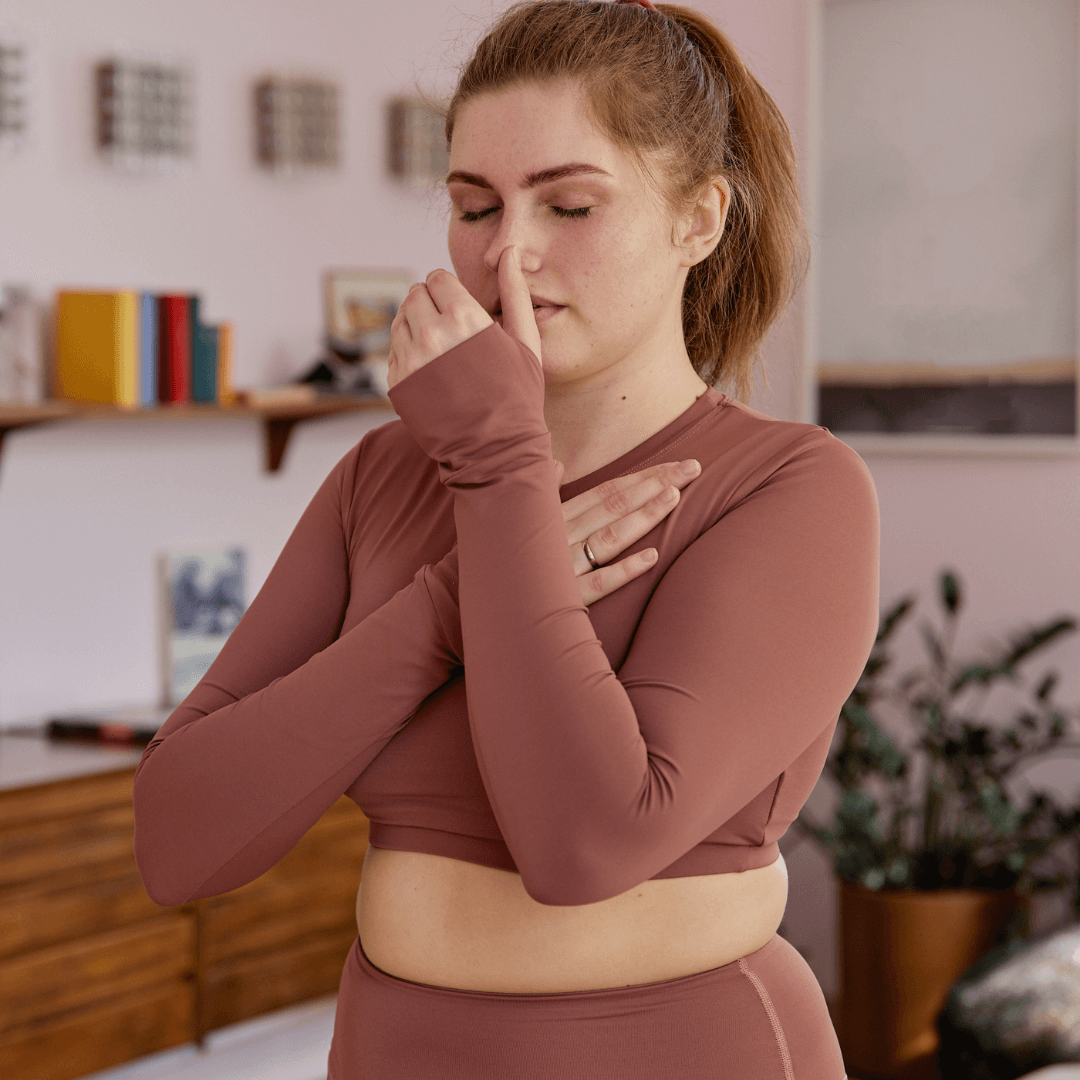

Breathing exercises are a powerful tool for stimulating the vagus nerve and promoting better sleep. By focusing on specific breathing patterns, you can activate the parasympathetic nervous system and induce a state of relaxation.
One effective breathing technique is the 4-7-8 method, also known as the "relaxing breath." This involves inhaling for 4 seconds, holding the breath for 7 seconds, and then exhaling for 8 seconds. This pattern helps to slow down the breathing rate, which can trigger the vagus nerve's relaxation response.
Another technique is alternate nostril breathing, or Nadi Shodhana. This involves gently closing off one nostril and breathing in through the other, then switching and exhaling through the opposite nostril. This rhythmic breathing pattern can help balance the autonomic nervous system and stimulate the vagus nerve.
Meditation and mindfulness practices to activate the vagus nerve
Meditation and mindfulness practices can be powerful tools for stimulating the vagus nerve and promoting better sleep. These practices often involve deep breathing, focused attention, and a state of calm awareness, all of which can activate the parasympathetic nervous system and the vagus nerve. Research shows that regular engagement in yoga and mindfulness practices can significantly enhance vagal tone and improve overall mental health by influencing the autonomic nervous system.
One particularly effective meditation technique for vagal stimulation is the practice of loving-kindness, or Metta meditation. This practice involves cultivating feelings of compassion, kindness, and goodwill towards oneself and others. By engaging in this form of meditation, you can stimulate the vagus nerve and promote a state of relaxation and well-being, which can significantly improve sleep quality.
Mindfulness-based practices, such as body scans and mindful breathing exercises, can also be effective in stimulating the vagus nerve. By bringing your attention to the sensations in your body and the rhythm of your breath, you can activate the parasympathetic nervous system and enhance vagal tone, leading to better sleep.
Other methods of vagal stimulation for better sleep

While breathing exercises and meditation are accessible and effective methods for stimulating the vagus nerve, there are also other techniques and interventions that can be explored for improved sleep.
One such method is the use of vagus nerve stimulation (VNS) devices. These devices, which are typically implanted under the skin near the collarbone, deliver mild electrical impulses to the vagus nerve, triggering a physiological response that can enhance sleep quality. VNS has been used to treat various conditions, including depression and epilepsy, and is now being studied for its potential benefits in improving sleep.
Another approach is the use of cold-water immersion or cryotherapy. Exposing the body to cold temperatures, such as by taking a cold shower or using a cryotherapy chamber, can activate the vagus nerve and trigger the parasympathetic nervous system's relaxation response. This can lead to a reduction in stress and anxiety, ultimately promoting better sleep.
Incorporating vagal stimulation into your bedtime routine
Integrating vagal stimulation techniques into your bedtime routine can be a powerful way to improve your sleep quality. By making these practices a consistent part of your nightly ritual, you can create a strong association between the activities and the onset of sleep, making it easier to transition into a restful state.
One approach is to begin your bedtime routine with a few minutes of deep breathing exercises or Nadi Shodhana. This can help calm the mind and body, setting the stage for a more restful night's sleep. You can then follow up with a brief meditation or mindfulness practice, such as a body scan or loving-kindness meditation, to further stimulate the vagus nerve and promote relaxation.
To enhance these relaxation techniques, consider preparing a cup of our Deep Sleep Tea, which contains ashwagandha—a powerful adaptogen known for its stress-relieving properties. Sipping on this soothing tea while engaging in these practices can further calm your nervous system, helping you unwind and prepare for a deep, restorative sleep. The ritual of brewing and enjoying Deep Sleep Tea] not only enhances the relaxation response but also signals to your body that it’s time to wind down, making the transition to sleep smoother and more natural.
Additionally, you can consider incorporating other vagal stimulation methods, such as gargling or humming, into your routine. These simple exercises can be done while your Deep Sleep Tea is steeping, helping to activate the vagus nerve and enhance the overall sleep experience.
Conclusion and final thoughts
The vagus nerve is a remarkable and multifaceted component of the human body, playing a crucial role in regulating a wide range of physiological processes, including sleep. By understanding the link between the vagus nerve and sleep, and by incorporating techniques to stimulate this important nerve, individuals can unlock the path to better, more restorative sleep.
From breathing exercises and meditation to more advanced interventions like vagus nerve stimulation, there are numerous ways to harness the power of the vagus nerve for improved sleep quality. By making these practices a consistent part of your daily and nightly routines, you can cultivate a stronger connection with your vagus nerve, leading to a more balanced autonomic nervous system and a more rejuvenating sleep experience.
As you embark on this journey of exploring the vagus nerve and its impact on sleep, remember that the path to better sleep is a personal one. Experiment with different techniques, find what works best for you, and embrace the transformative power of the vagus nerve as you unlock the secrets to a more restful and rejuvenating slumber.